How Much Control Can You Give AI Agents Before AI Ethics Become Relevant?

We're seeing something really exciting happen in the world of software right now: the rise of "agentic AI." These smart systems can handle complex tasks and reach goals with just a little help from us. Whether it’s in IT, HR, customer service, or other areas, AI agents are being customized to fit the unique needs of different teams. But as they get more capable, a big question starts to pop up: how much control are we giving up, and what does that mean for us, and is ethical AI something to worry about?
Let’s take a closer look at the range of AI autonomy, checking out the upsides and the downsides and highlighting why AI ethics matter as we use AI agents in our day-to-day lives.
What Are AI Agents?

Source: TMT Predictions 2025
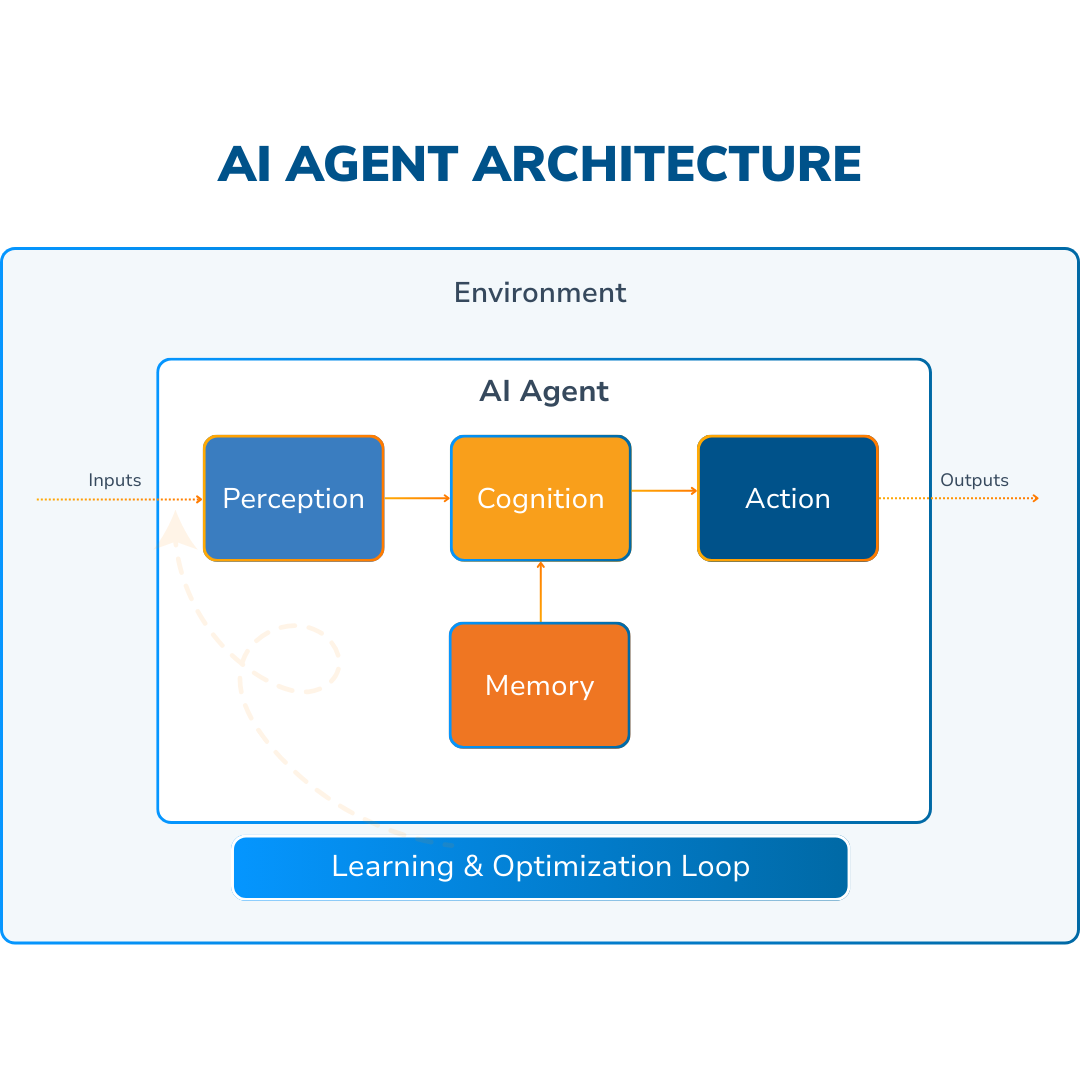
To put it simply, an AI agent is like a smart helper that can take care of tasks for you, working independently to get stuff done. These systems design their own workflows and make good use of the tools they have at their disposal. Here’s what they do at their core:
- Perception: They make sense of their surroundings by processing different types of data, like text, images, sounds, and more.
- Cognition: After collecting data, they interpret it with machine learning models, especially neural networks that have been trained on extensive datasets.
- Decision-Making: They figure out the best way to go about achieving their goals based on what they observe.
- Action: They follow through by completing tasks or providing answers based on the choices they’ve made.
These agents are usually created using techniques like supervised learning (learning from labeled examples) and reinforcement learning (learning through trial and error with rewards).
“Deloitte predicts that by 2025, around 25% of companies using generative AI will start exploring projects with agentic AI. And this number might climb to 50% by 2027. Some of these applications could even begin weaving into daily operations by the end of 2025.”
Investors are getting in on the action, too, pouring over $2 billion into startups, especially those aimed at enterprise solutions. At the same time, big tech companies and cloud providers are not just creating their own agentic AI features; they’re also making smart acquisitions and partnering with startups, often opting to license technology or hire talent rather than buy the whole company.
There are many kinds of AI agents. We have familiar tools, like chatbots for customer interactions, handy virtual assistants that can handle our schedules and reminders, and even cutting-edge tech like autonomous vehicles on the road. For example: An AI agent working in a contact center. It chats with customers, pulls up information from internal databases, and offers solutions. If things get a bit too complicated, it knows to hand off the tough stuff to a human agent.
The Power of AI Agent Assistance: Why We’re Drawn In
It’s difficult to resist AI agents. Yet, while these tools come in handy, use them with caution. You see, leaning too heavily on AI might mean we’re not keeping an eye out like we should be. There is a chance that mistakes or biases will pop up. As long as you catch these issues ahead of time, we can tackle them beforehand and experience its transformative power in different areas:
Customer Experience:
AI agents are changing the way businesses connect with customers through virtual assistants, mental health support bots, and interview simulators. They offer quick, helpful support and are easy to set up using no-code templates.
Healthcare:
AI agents are revolutionizing patient care by streamlining treatment planning in emergency situations and improving how medications are managed. This lets healthcare pros focus on what’s urgent, leading to better patient outcomes.
Emergency Response:
During crises, AI agents analyze social media to find people in need during natural disasters. They help map locations, allowing emergency services to respond faster and potentially save lives.
Finance and Supply Chain:
AI agents crunch real-time financial data, predict market trends, and optimize supply chains. Their flexibility provides tailored outputs, making financial analysis more efficient and secure.
Tech Companies:
Big tech firms are leveraging AI agents to enhance their products and services. They boost software capabilities and create new ways for customers to interact, driving growth and efficiency.
Isn’t it fascinating?

(Source: Deloitte)
Finding the Balance Between the Upside and Downside of Agentic AI
While the perks of AI agents are hard to ignore, our growing dependence on them means we need to think carefully about the ethical concerns of AI. Relying too much can lead us to overlook important details, and we can’t forget that AI decision-making might include errors or biases. That's why it's vital to spot and tackle these challenges head-on for responsible AI use.
How SJ Innovation Combines AI and Humans in Different Departments?
At SJ Innovation, we focus on bringing out our human abilities with AI, rather than completely relying on it. Here’s a closer look at how we add AI into various departments, while also keeping that essential human touch alive.
Project Management
- We lean on AI agents to tackle tasks such as crafting user stories, generating reports, and summarizing lengthy meetings.
- This way, project managers can breeze through routine paperwork and focus on the bigger picture.
- Our project managers double-check the AI agents’ outputs to ensure accuracy.
- They bring their insights and experiences to the table, ensuring every decision is well-informed and human-centered.
Sales and Marketing
- When it comes to marketing, our AI agents pitch in by brainstorming content ideas, digging up SEO keywords, and even writing copy for blogs, social media, and emails.
- Our marketing crew fine-tunes the messaging, ensuring it matches our brand's unique tone.
- AI also helps analyze customer data to spot trends, but it’s our team that interprets those insights and crafts strategies that truly connect with our audience.
- Our designers use AI for project-specific templates and creative exploration, but it’s their artistic touch that brings our brand's visuals to life.
Human Resources
- In HR, we’ve got some fantastic AI agents tracking employee skills and aspirations.
- They manage a database that helps us figure out how to best utilize our talent.
- They interpret the AI’s suggestions, combining their knowledge of our company culture with a people-first approach to make thoughtful decisions about development.
- Plus, with AI streamlining onboarding tasks, our HR team ensures new hires feel welcomed and ready to succeed.
- Tools like Google Sheets or Excel can be a bit daunting, so we use AI to handle those tricky formulas.
Quality Assurance and Development
- In QA and development, AI helps spot errors and analyze code, which makes catching potential issues easier.
- Our developers then take charge and interpret these insights and accordingly make decisions.
- They rely on AI for the repetitive tasks so they can spend more time on the creative aspects of coding and developing new features.
In this way, we make sure that AI and ethics are in control.
The Risks of Total Control: What Could Go Wrong?
That said, we have to be aware of AI and ethics and the significant risks that come with letting AI operate unchecked:
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can carry over biases from their training data, which can lead to unfair or biased outcomes.
- Cascading Failures: When AI systems are linked together, mistakes can turn into bigger issues. So, having solid testing and backup plans is super important.
- Accountability Gaps: It can be tough to figure out who’s responsible when AI makes a mistake, so we need clear human oversight and rules for intervention.
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems can be targets for cyberattacks, making it crucial to have strong security measures and response plans in place.
- Human Deskilling: Relying too heavily on AI may cause people to lose their skills, so ongoing learning and skill development are key.
Autonomy vs. Control: Reimagining the Human-AI Partnership

The connection between humans and AI really runs along a spectrum, making us rethink how we view accountability and control. This spectrum goes from semi-autonomous AI, which suggests actions for us to approve, to supervised autonomous AI, where systems make decisions within certain guidelines, all the way to fully autonomous AI that operates independently.
What's interesting is that having more autonomy for AI doesn’t mean we have less control; instead, it changes the kind of control we have. We shift from direct control over daily decisions to a broader control that shapes the system's goals and values. So, the key question isn’t just whether we can control AI, but how we can effectively guide and influence what it does.
To keep this balance in check, we need solid oversight measures, including:
- Transparency: Making sure AI decision-making is understandable.
- Auditability: Keeping records of AI behavior for review.
- Interruptibility: Allowing humans to step in and override AI actions when needed.
- Value Alignment: Ensuring AI systems reflect our human priorities and ethics.
Real-World Fallout: The Risks of Unchecked AI
The risks tied to AI agents become pretty clear when things go wrong:
- The Uber Tragedy: In Arizona, an Uber self-driving car struck and killed a pedestrian after its perception system failed to identify her correctly.
- Flawed Exam Results: In 2020, UK teachers faced an algorithm that unfairly downgraded students' results based on socioeconomic factors, impacting their futures without a chance for appeal.
- Harmful Healthcare Advice: A 2023 AI chatbot advised patients with serious symptoms to rest rather than seek emergency care, due to flawed training focused on cost containment.
- Content Moderation Gone Wrong: AI content moderation removed accounts sharing evidence of human rights abuses because it couldn’t differentiate between reporting violence and promoting it.
- Privacy Concerns: The massive amounts of data AI needs can lead to constant surveillance and the possibility of leaking sensitive information. The Cambridge Analytica scandal is a stark reminder of this.
- Job Displacement and Economic Shift: AI is increasingly able to automate tasks we once thought were safe, risking job losses and widening economic gaps, as shown by the 2023 Goldman Sachs analysis.
Real-World Fallout: The Risks of Unchecked AI
The risks tied to AI agents become pretty clear when things go wrong:
- The Uber Tragedy: In Arizona, an Uber self-driving car struck and killed a pedestrian after its perception system failed to identify her correctly.
- Flawed Exam Results: In 2020, UK teachers faced an algorithm that unfairly downgraded students' results based on socioeconomic factors, impacting their futures without a chance for appeal.
- Harmful Healthcare Advice: A 2023 AI chatbot advised patients with serious symptoms to rest rather than seek emergency care, due to flawed training focused on cost containment.
- Content Moderation Gone Wrong: AI content moderation removed accounts sharing evidence of human rights abuses because it couldn’t differentiate between reporting violence and promoting it.
- Privacy Concerns: The massive amounts of data AI needs can lead to constant surveillance and the possibility of leaking sensitive information. The Cambridge Analytica scandal is a stark reminder of this.
- Job Displacement and Economic Shift: AI is increasingly able to automate tasks we once thought were safe, risking job losses and widening economic gaps, as shown by the 2023 Goldman Sachs analysis.
What to Know About Ethical AI?

With great power comes great responsibility. As AI agents become increasingly autonomous and capable, the ethical implications of their use grow more profound. Ethics isn't just an academic exercise—it's the practical framework that determines how we ensure these powerful tools serve humanity rather than harm it.
The Ethical Imperative
AI systems have woven themselves into many areas that touch our lives: healthcare, loan approvals, hiring processes, criminal justice, and beyond. When these AI systems make decisions or influence outcomes in such critical fields, the stakes couldn't be higher. Just think about these real-life examples:
- An insurance claims AI that unfairly turns away applicants from specific zip codes, echoing historical discrimination patterns.
- A healthcare triage algorithm that prioritizes patients based on how much they've spent in the past, rather than their actual medical needs.
- A recruitment tool that unintentionally weeds out capable candidates simply because they don’t fit the profiles of past hires.
The data fueling these systems often includes hidden biases. Without ethical oversight, these biases can grow larger and become entrenched in the process. This isn’t just a hypothetical situation—it’s happening right now.
Four Pillars of Ethical AI Implementation
To create ethical AI, we need thoughtful design and governance in four key areas:
- Fairness and Non-discrimination
- Test AI systems for their effects on different demographic groups.
- Use strategies like adversarial debiasing and fairness checks during development.
- Keep an eye on potential biases even after the systems are live.
- Transparency and Explainability
- Build systems where decisions are clear and easy to understand.
- Create “audit trails” for important AI decisions.
- Make sure individuals know why decisions were made concerning them.
- Human Oversight and Intervention
- Design systems that include humans in the loop for sensitive situations.
- Set clear guidelines for when human judgment should step in over AI suggestions.
- Ensure there’s genuine oversight, rather than just approving automated choices.
- Accountability and Governance
- Define clear responsibility for AI-driven results.
- Create strong appeal processes for those affected by AI decisions.
- Promote organizational structures that support ethical AI development.
Beyond Compliance: A Values-Based Approach
True ethical AI isn’t just about following rules; it’s about diving deeper into what we believe in:
- What results are we aiming for, and do those serve the greater good?
- Who benefits from our AI systems, and who could be negatively impacted?
- Are we crafting technology that respects human agency and dignity?
- How do we balance pushing for innovation while being cautious in uncharted ethical waters?
The Path Forward
As AI agents grow more capable, the line between “tool” and “autonomous actor” gets blurrier. This doesn’t lessen our responsibility; if anything, it heightens it. Organizations using AI must:
- Regularly assess the ethical impact of their systems.
- Build diverse teams for AI development and oversight.
- Engage with stakeholders and communities affected by their AI decisions.
- Keep up with the latest best practices in AI ethics.
- Help shape industry standards and frameworks.
The real potential of AI isn’t just in its tech abilities but in how it aligns with and promotes human values. By incorporating ethical considerations from the start—rather than viewing them as an afterthought—we can build AI systems that earn our trust and genuinely enhance human well-being.
What do you think about balancing AI autonomy with human control? I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments below!

Be productive using tools and techniques.

What Makes You Unique In A Job Interview


