How to Protect Your Applications in the Cloud with AWS Armor

In this age where everything seems to be in the cloud, keeping our digital stuff safe from cybercriminals is a pretty big deal. Just think about what a data breach or even some downtime could cost you. Research shows that attacks on cloud apps are shooting up, costing companies a whole lot of cash—like, we're talking millions here. That's why it's not just a nice idea to safeguard your applications; it’s something you absolutely have to do.
Here’s where AWS Armor comes into play. This post will look at how AWS Armor steps up to guard your applications running on AWS. It defends against tricky attacks, like the ones that flood your site with traffic (known as DDoS) or sneak in through databases (like SQL injection), helping to keep your app running smoothly and reliably.
Understanding AWS Armor

AWS Armor isn't a single tool but a powerful combination of three key AWS services:
- AWS Shield:
- This is your shield against attacks that try to drown your application with too much traffic—those pesky Distributed Denial of Service, or DDoS, attacks.
- AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall):
- Stops the bad requests from getting into your app. It blocks things like SQL injection attacks, which try to exploit weak spots in your database, and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), where attackers try to sneak in harmful scripts onto your site.
- AWS Firewall Manager:
- Helps manage security settings across different AWS accounts, making sure everything is protected in the same way.
All these services work together, keeping your applications safe and ensuring they’re always available on AWS.
Why is Cloud Security Non-Negotiable?
As more businesses shift their applications to the cloud, concerns about security are only growing. Just think about what a data breach or unexpected downtime could mean for your reputation and your finances. Believe it or not, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was over $4 million! Clearly, these threats are serious, and they call for proactive action. That’s where AWS Armor steps in. It offers robust security solutions that help you prevent, detect, and address risks.
With today’s reliance on APIs, serverless computing, and microservices, the potential for attacks keeps expanding. AWS Armor is designed to keep your applications safe while ensuring they perform well and stay available.
AWS Shield, AWS WAF, and AWS Firewall Manager: What’s the Difference?
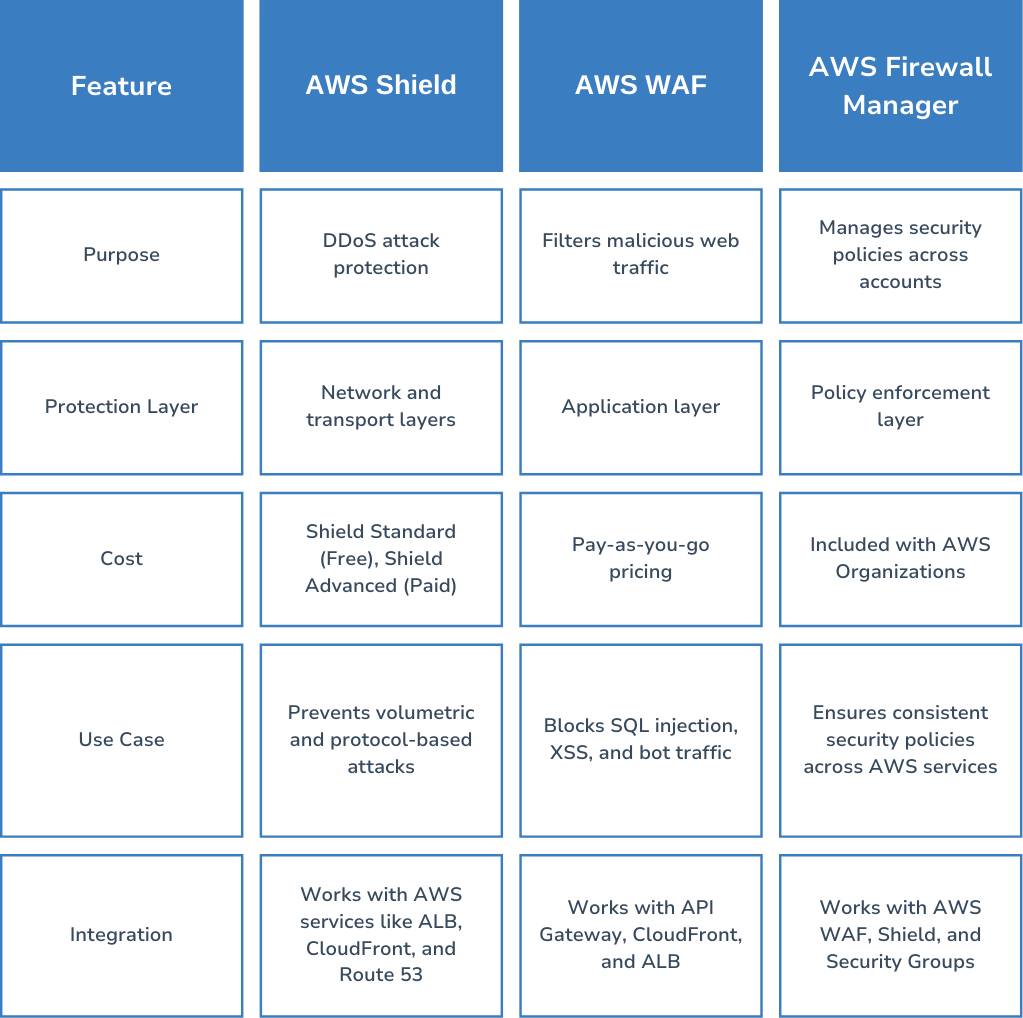
- Network and transport layers: This is where AWS Shield comes into play, safeguarding against attacks that aim to flood your network.
- Application layer: This is where AWS WAF protects your web applications from targeted attacks.
- Policy enforcement layer: AWS Firewall Manager makes sure that your security rules are applied consistently across your AWS environment.
AWS Shield: Protecting Against DDoS Attacks

DDoS attacks aim to flood your application with so much traffic that it becomes slow or even unavailable. AWS Shield provides two levels of protection:
- AWS Shield Standard (free): This automatically shields your applications from common DDoS attacks targeting the network layer.
- AWS Shield Advanced (paid): For those looking for enhanced protection, this level offers better detection, real-time visibility during attacks, and cost protection if you're targeted.
By enabling AWS Shield on services like Elastic Load Balancer (ELB), CloudFront, and Route 53, you can safeguard against various types of attacks. Businesses that see significant traffic spikes and operate across the globe will especially benefit from these proactive measures.
AWS WAF: Filtering Malicious Web Traffic

AWS Firewall Manager lets you oversee security rules across multiple AWS accounts and applications, ensuring that your policies are enforced consistently. This feature is especially helpful for businesses with various AWS-hosted applications and offers:
- Automatic policy enforcement for AWS WAF and Shield.
- Auditing of security groups to catch misconfigurations.
- Multi-account support through AWS Organizations.
Setting Up AWS WAF for an Application
So, you want to set up AWS WAF for your application? Here’s a simple guide to get you started:
- Create a Web ACL: First off, hop into the AWS Console and set up a Web Access Control List (ACL) for AWS WAF. This will be the backbone of your security settings.
- Define Your Security Rules: Next, think about the specific security measures you want to implement. For example, you might want to block any traffic from suspicious user agents or limit access to certain IP addresses. Tailor these rules to suit your application’s needs.
- Link the Web ACL: Once your rules are in place, associate the Web ACL with AWS services like CloudFront or Application Load Balancer (ALB). This connection ensures your security settings are effective where they count.
- Keep an Eye on the Logs: After everything is set up, don’t forget to monitor the logs regularly. This will help you spot any suspicious activity and refine your security policies over time.
AWS Firewall Manager: Centralized Security Management

Now, let’s talk about AWS Firewall Manager. This tool helps manage security across multiple AWS accounts and applications. Here’s what it brings to the table:
- Automatic Policy Enforcement: With Firewall Manager, there’s no need for constant manual updates. It automatically applies your security policies for AWS WAF and Shield, saving you time and effort.
- Security Group Auditing: It also helps you keep track of your security groups, flagging any misconfigurations that could leave your applications vulnerable.
- Multi-Account Support: If your business runs multiple AWS accounts, you’re in luck! Firewall Manager supports management through AWS Organizations, making it easier to enforce consistent security practices across the board.
Best Practices for Securing an Application with AWS Armor
- Use AWS Shield Standard for basic DDoS protection.
- Enable AWS WAF rules to filter out harmful requests.
- Implement security headers to block XSS attacks.
- Secure API requests with authentication and rate limiting.
- Use AWS IAM roles to limit access to sensitive services.
- Keep an eye on traffic and analyze logs for suspicious activity in real time.
My Experience as a MERN Stack Developer: Securing APIs with AWS WAF
“As a MERN stack developer, I encountered security challenges when deploying applications on AWS. One of the biggest concerns was protecting the backend APIs from malicious traffic and preventing unauthorized access. During a project where I built a customer management system, we faced issues with bot traffic and attempted SQL injections targeting our API Gateway.
To mitigate these risks, we implemented AWS WAF to filter requests based on predefined rules, blocking suspicious activity before it could reach our backend. Additionally, AWS Shield helped protect the application from unexpected DDoS attacks, ensuring uptime even during traffic spikes. Managing security policies across multiple environments became easier with AWS Firewall Manager, allowing consistent enforcement of security rules across all deployed instances.
By using AWS Armor, we improved the security posture of our application, reduced attack surface, and maintained high availability without compromising performance. These tools provided peace of mind and allowed us to focus on feature development rather than constant security monitoring.”
Real-World AWS Armor Use Cases
- E-commerce platforms: Use Shield Advanced for sudden traffic spikes.
- Financial institutions: Use WAF to prevent data breaches.
- Media networks: Use Firewall Manager for consistent security across regions.
- Healthcare and banking: Use AWS Armor for regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
AWS Armor offers a suite of powerful security services that protect your applications in the cloud. By using AWS Shield, AWS WAF, and AWS Firewall Manager, you can effectively defend against cyber threats and ensure your applications stay available. Integrating these security measures is key to achieving lasting stability and resilience.
As businesses grow and cyber risks become more sophisticated, adopting proactive security strategies like AWS Armor is more than a good idea; it’s critical. Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, investing in cloud security today can save you from expensive breaches and downtime down the line.
With AWS Armor in your corner, you can confidently focus on scaling your application without the constant worry of security vulnerabilities. Don’t wait for an attack to happen—connect with our AWS experts and start protecting your AWS applications today!

THE MODERN TOOL: CYPRESS

Quality Risk Analysis Hackathon


