Why is Data Protection in Healthcare IT a Critical Imperative?

The digital age in healthcare is a double-edged sword. On one side, technology such as electronic medical records, telemedicine, and AI-powered diagnostics paves the way for accessibility for all and innovation that was unimaginable 10 years ago. On the other hand, these healthcare organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive data - from medical records to insurance details - so the question arises, “Do healthcare organizations protect patient privacy?”
After all, you can’t ignore the surge in data breaches that not only put patient privacy in jeopardy but also trust and quality care. This blog takes a look at healthcare data security, exploring its challenges and best practices.
The Disturbing Trend of Rising Healthcare Data Breaches
The numbers are stark and revealing: the frequency of healthcare data breaches has seen an upward trend over the past 14 years. 2021 was a horrendous year experiencing a significant loss of 45.9 million records. In 2022, the situation was worse with 51.9 million breached records, and then in 2023, the industry faced a record-breaking breach of an alarming 133 million records exposed, stolen, or impermissibly disclosed. This breach in sensitive healthcare information underscores a pressing need for robust cybersecurity measures in the healthcare sector.
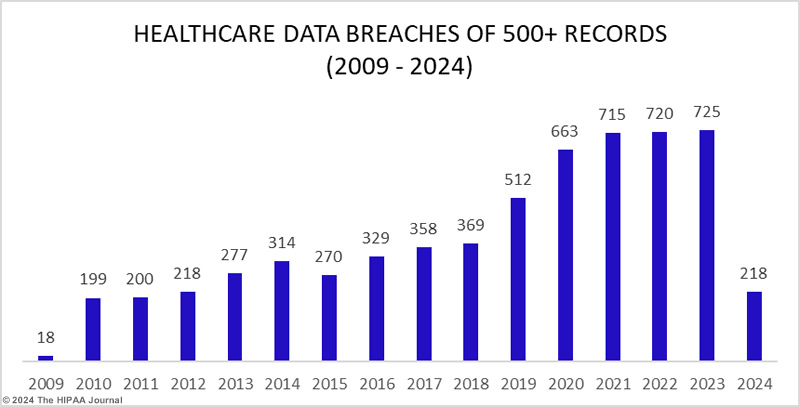
Healthcare Records Exposed by Year
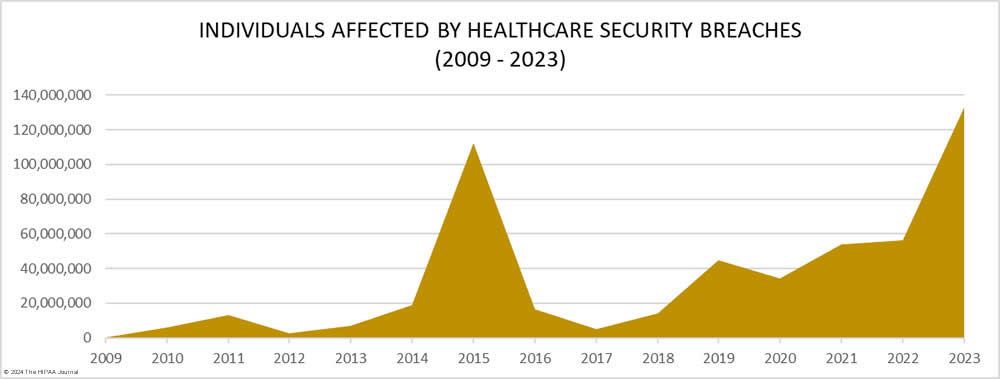
(Source: The HIPPA Journal)
Ransomware and device vulnerabilities resulting in longer hospital stays
Then, another issue arises: inherent device vulnerabilities that contribute to extended hospital stays. On average, medical devices are reported to have 6 vulnerabilities, with 60% being at the end-of-life stage. A survey revealed that nearly 70% of healthcare organizations experienced longer hospital stays and delays in procedures owing to ransomware attacks.
Key Drivers of Cyber Insurance Claims in Healthcare:
- Accidental Data Breaches: 29%
- Malicious Data Breaches: 18%
- Stolen or Lost Devices: 16%
- Ransomware: 8%
What is Healthcare Data Security?

Healthcare data security ensures the integrity and privacy of patient data across computers and networks used by providers and insurers. One of the key driving factors for stringent data security practices in healthcare is Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). HIPAA sets the bar for how sensitive patient data must be handled.
Why is Healthcare Data Security important?
“90% of healthcare organizations have experienced 1 security breach, with 30% occurring in large hospitals.”
Here is why healthcare data security matters:
Unauthorized access is risky: Patient records contain delicate information - medical conditions, treatment plans, and identifying details. When accessed without authorization, this information could lead to identity theft and insurance fraud.
The aftereffects of data breaches: The fallout from a data breach isn’t just digital. It erodes the trust that patients place in healthcare systems, comes with significant legal penalties, and may interrupt essential healthcare services. A scenario where a cybercriminal disrupts access to electronic health records is more than just a breach of privacy—it's a potential threat to patient welfare.
Challenges and Solutions in Healthcare Software Product Development
#1 Managing Compliance and Regulations in Healthcare Software is Tough!
The healthcare industry is governed by a complex web of regulations that software development teams must navigate. Different regions have different laws and standards around security, privacy, and quality of healthcare data and software.
In the US, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the guidelines, while in the EU, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the governing body. Adhering to these regulations is a daunting task for medical software development teams.
The Solution
To overcome this challenge, healthcare software development teams must take the following steps:
- Engage in continuous learning to stay up-to-date with ever-changing regulations and best practices.
- Collaborate with experts who are well aware of healthcare application categories, regional requirements, medical device classification, data protection, and clinical validation.
- Adopt standards like HL7 FHIR, MedMij, and DICOM to streamline the compliance process and ensure interoperability with other systems. These standards provide a common framework for exchanging, storing, and processing healthcare information.
- HL7 FHIR: Adopt this for streamlined and effective health data exchange.
- MedMij: Use this standard to meet Dutch data-sharing regulations.
- DICOM: Integrate this for proper management and transmission of medical imaging.
#2 Care Mobility and Scalability in Healthcare Software is Challenging
In today's fast-paced world, patients expect to access their health information and services anytime, anywhere, and on any device. Healthcare professionals demand software that is compatible across devices and platforms, with the ability to scale up or down as needed.
Developing software that meets these expectations is a significant challenge in healthcare software product development, as it requires addressing various factors, including user interface design, performance optimization, data synchronization, security, and compatibility. Additionally, the software must be thoroughly tested on different devices and platforms to ensure it can handle varying loads and traffic.
The Solution
- Focus on developing cross-platform applications and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) to provide a seamless user experience across devices and platforms.
- Leverage cross-platform technologies that can run on multiple operating systems, such as Windows, iOS, and Android.
- Implement PWAs, which are web applications that can be installed on users' devices and offer features like offline access, push notifications, and fast loading.
- By adopting these technologies, healthcare software developers can ensure their solutions are accessible, responsive, reliable, and scalable.
- Use a single codebase for multiple platforms, reducing development time and costs.
#3 Responsive and User-friendly UI/UX Design in Healthcare Products is rare
Healthcare apps are used by a diverse range of individuals, from patients to medical professionals. Designing these apps to be genuinely helpful, responsive, and intuitive is a significant challenge.
Many healthcare apps fail to address the real needs and preferences of patients, such as convenience, accessibility, personalization, and engagement. They also lack user-friendly and attractive interfaces that can enhance the overall user experience and satisfaction.
The Solution
- Integrate interactive communication tools, such as video conferencing, online appointments, and voice chats, to enable better communication and collaboration between patients and healthcare professionals.
- Continuously refine the healthcare UI/UX design by collecting feedback from patients and professionals, and applying user-centric design principles and best practices.
- Ensure that healthcare apps are helpful, engaging, and easy to use, catering to the diverse needs of their target audience.
#4 Privacy and The Risk of Medical Data Breaches is an Issue
The healthcare industry deals with a significant amount of sensitive data, making the utmost security and privacy of critical medical data a paramount challenge. Medical data is highly sensitive and personal, subject to various threats, such as cyberattacks, data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse. These threats can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of medical data, causing serious harm to patients and healthcare organizations.
The Solution
- Implement comprehensive security measures, from the interface level to deeper layers, including multi-factor authentication, automatic log-offs, and data encryption.
- Seamlessly integrate with systems like HIS, RIS, and PACS for secure medical data access.
- Follow best practices and standards for data protection and security, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 27001.
- Ensure that healthcare software is secure, compliant, and trustworthy, protecting the privacy and integrity of sensitive medical data.
#5 Specific Customization Needs for Healthcare Software is Not Present
Every healthcare provider has unique requirements, workflows, processes, policies, and preferences that need to be reflected in their software solutions. Standard software rarely meets these specific needs, leading to inefficiency, frustration, and dissatisfaction among healthcare providers.
The Solution
- Collaborate with business analysts experienced in eHealth projects to understand the specific needs of each healthcare provider.
- Tailor software solutions to meet the expectations and requirements of individual healthcare providers.
- Develop customized healthcare software solutions that improve functionality, usability, performance, and compatibility.
- Provide a competitive edge and unique value proposition for healthcare providers by offering tailored solutions.
#6 There are Data Integration Issues in Health Software Product Development
Healthcare facilities deal with various data sources, such as electronic medical records (EMRs), laboratory information systems (LISs), medical imaging systems, wearable devices, and mobile apps. These data sources often have different formats, standards, and protocols, making it difficult to integrate and synchronize them. Data integration issues can affect the quality, accuracy, and completeness of healthcare data, hampering decision-making and the coordination of care.
The Solution
- Prioritize the development of software that offers seamless integration and synchronization across different systems.
- Utilize common data models, formats, and standards, such as HL7 FHIR, MedMij, and DICOM, to facilitate data exchange and interoperability.
- Emphasize the advantages of medical device software that can reduce errors and ensure real-time monitoring.
- Implement solutions that enable efficient and accurate data integration, supporting informed decision-making and coordinated care.
Protect Your Patients, Preserve Trust: Take Action on Healthcare IT Security Now
Our exploration into healthcare data security is a wake-up call for action. The startling rise of data breaches, device vulnerabilities, and increasing ransomware attacks underline the urgency for ironclad cybersecurity measures. Now is the time to prioritize data protection in your healthcare IT environment. Ensure that patient privacy isn't just a policy but a steadfast practice within your organization. Take the necessary steps to safeguard sensitive information, starting with implementing a robust cybersecurity framework that can withstand the complexities of the healthcare domain.
Don't let another record fall prey to breaches. Enhance your healthcare data security today. Contact our healthcare software development experts for comprehensive strategies and solutions that ensure your patient's data remains secure and your reputation intact

Why Do We Debug Code?

Sjinnovation’s Project Management Process


